Wireless charging explained! Everything you need to know،
Wireless charging. It is magic. It is a testimony to technological progress. It's pure science fiction! Okay, let's stop the drama for a bit. You get home, unzip, and throw your smartphone on the charger. What is really happening? How does all that energy get from the charger to the phone through the air, without any cables? Today we're going to find out!
Electromagnetic induction
We're going to take you back to high school, but we promise it won't be boring. Electromagnetic induction was discovered almost 200 years ago by a man called Michal Faraday in 1831. He played with copper wires and magnets and discovered that passing voltage through a wire caused strange things with the other wire, even though they weren't connected to the other wire. another.
The first wireless charger for smartphones, around 1831
We now know that a moving electric charge generates a magnetic field. That's the basic principle behind it all. When electrons move through the copper wire, a magnetic field is generated; This is how electromagnets work. Now if you place another copper coil near the first one and adjust its position, number of wires, gauge, etc., it will pick up this magnetic field and electrons will start moving in this second coil.
This energy transfer is special because it does not require support. Your smartphone charger will work in the vacuum of space. This is because the electromagnetic field is everywhere around us, even in the vacuum of space.
As you go around with the coil and the electrical charge, it will create a disturbance in that field, much like throwing a stone into a perfectly still lake. The difference is that, unlike the lake, the electromagnetic field is not a medium in itself. It's just a property of space.
What is a wireless smartphone charger?
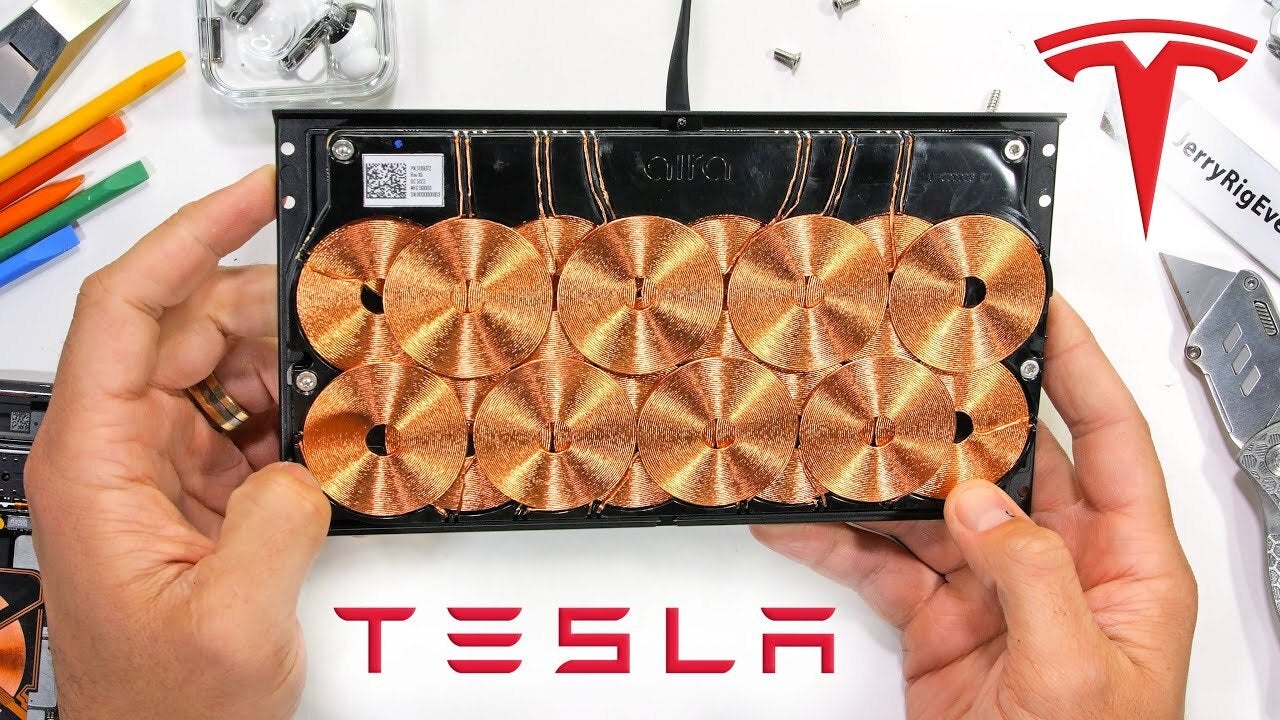


The Tesla wireless charger and its 16 coils. Image – JerryRigAll
You may have watched videos where people have taken apart these chargers or even done it yourself. Wireless smartphone chargers are made of tiny copper coils that transfer energy to a similar system inside your phone: a thin copper coil placed just under the back cover.
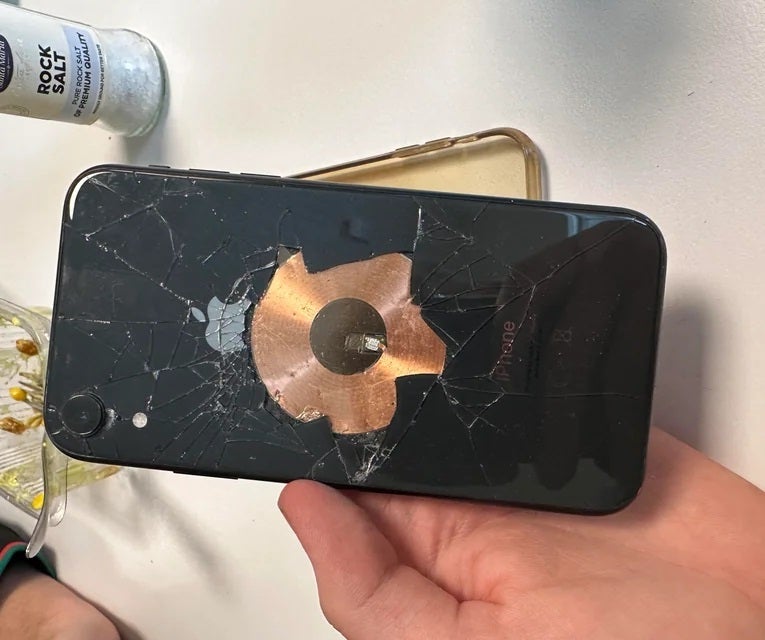


No need to crack your phone to check if we're right. Trust us on this
The two coils must be properly aligned for energy transfer to occur. You may have experienced this yourself, trying to find the right sport for your phone on the charger. More sophisticated wireless chargers (Tesla's comes to mind) have multiple coils to allow charging wherever you place your phone on the charger.
Wireless charging standards


Transferring electricity over the air is no joke, and there need to be standards telling companies how to do it safely and also allowing wireless chargers to work universally (well, almost) with all gadgets supporting wireless charging.
Qi is the leading wireless standard developed by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) for inductive charging over distances up to 40mm. We will not go into the history of the standard and all the administrative and legislative aspects; The important thing to know is that this standard (pronounced chee, by the way) has been widely adopted by smartphone manufacturers.
Samsung, Apple, Sony, Honor, Oppo, OnePlus, Huawei, Nokia (HMD), Motorola and Xiaomi have integrated Qi wireless charging into their devices.
Wireless charging speed
Qi encompasses three distinct power specifications, with a primary focus on low power for charging mobile devices. Currently, different wattages are applicable, ranging from a minimum of 5W to some devices supporting 7.5W, 10W and even up to 15W, with a later version of the standard reaching 30W.


Honor courageously transfers 100W by induction!
It's worth noting that some companies have developed proprietary technologies to achieve faster wireless charging speeds. For example, Oppo and OnePlus offer wireless charging capabilities of up to 50W, while Honor has pushed the limits to 100W with the Honor Magic series.
These high-speed charging options, however, require a proprietary charging stand provided by the respective company and may not be universally supported by third-party manufacturers.
What are the advantages of wireless charging?
Well, you may have already guessed the convenience part of the equation. It's easy to just drop your phone on a charging mat and forget about it. There is much more! Here are all the benefits summarized:
- A simple and convenient way to charge your phone without having to worry about cables (sort of)
- Preserves the USB-C port, one of the most vulnerable points on your phone
- You can have wireless charging in your car, integrated into your work desk, portable wireless chargers, batteries with wireless charging: it's everywhere!
What are the disadvantages of wireless charging?
There is a price to pay when you want to transfer energy using the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Most metals are ferromagnetic and interfere with wireless energy transfer (the magnetic field interferes with the electrons inside and causes them to move; they have nowhere to go and the shaking creates heat). And there are still cables, unless you're using a portable battery pack with wireless charging support. Here are the disadvantages summarized:
- Not all phones have wireless charging
- It's difficult to continue using your phone while charging it wirelessly
- Wireless charging is (even) slower than wired charging
- Wireless charging is why we don't have metal phones anymore
- Most wireless chargers (except batteries) still require cables to plug into a power source
What's next for wireless charging?
The principle discovered by Faraday almost 200 years ago can be applied in many different scenarios. This is the principle of the electric motors that we use everywhere, from our vacuum cleaners to our Teslas (for the lucky ones of us who own one).
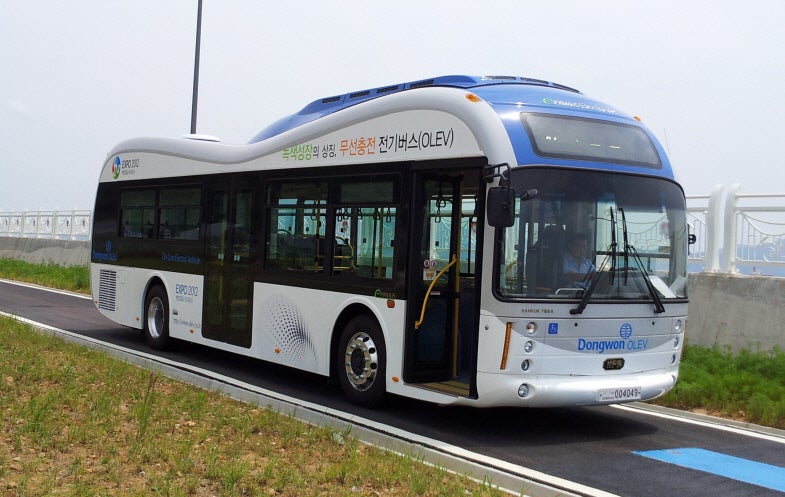


The Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) bus
Inductive charging has also been used to power much larger objects. There is a bus in South Korea that drives on a strip of road containing charging coils. Nicola Tesla himself conducted strange and dangerous experiments, transferring large amounts of energy over long distances.
There are fundamental limitations when it comes to transferring power in this way. If you want to do this over a long distance, you need a very strong magnetic field, and this can be dangerous for living creatures.
But technology is evolving, and one day we might have a universal wireless charging hub in our home that will be able to charge all of our gadgets, no matter where they are, without frying us in the process. Crossed fingers!
















