What is Wi-Fi 6E: Everything you need to know،
Gone are the days of slow and limited wired Internet connections. Some of you may remember dial-up modems with their strange and confusing sounds, but today we live in the wireless age. Wi-Fi is everywhere around us, and we are so used to it that we never ask ourselves the question: what exactly is Wi-Fi? The latest iteration of this wireless standard for data transfer is called Wi-Fi 6E, and today we're going to break it down and explain everything about it. But to get there, we have to start from the beginning.
What is Wi-Fi?
The nonprofit Wi-Fi Alliance coined the term “Wi-Fi” to describe a set of wireless networking protocols anchored in the IEEE 802.11 networking standard. Although Wi-Fi has been around since the late 1990s, its significant advancements have occurred in the last decade. The acronym stands for Wireless Fidelity and uses electromagnetic waves to transfer information wirelessly. We will explain the basic principle to you very quickly. Don't worry, no math will be involved.
Electromagnetic waves
Just like radio, Wi-Fi uses electromagnetic waves to transmit information. The wave is a disturbance of the electromagnetic field and it “wiggles” with a certain frequency. This is important because frequency is directly related to the amount of information an electromagnetic wave can carry.
Without getting too technical, let's give an example. We measure the frequency of a radio wave in hertz. 1 Hz means one complete cycle of the wave (one wave from start to finish) for one second. In other words, the higher the frequency, the more cycles or oscillations the wave completes in a second.
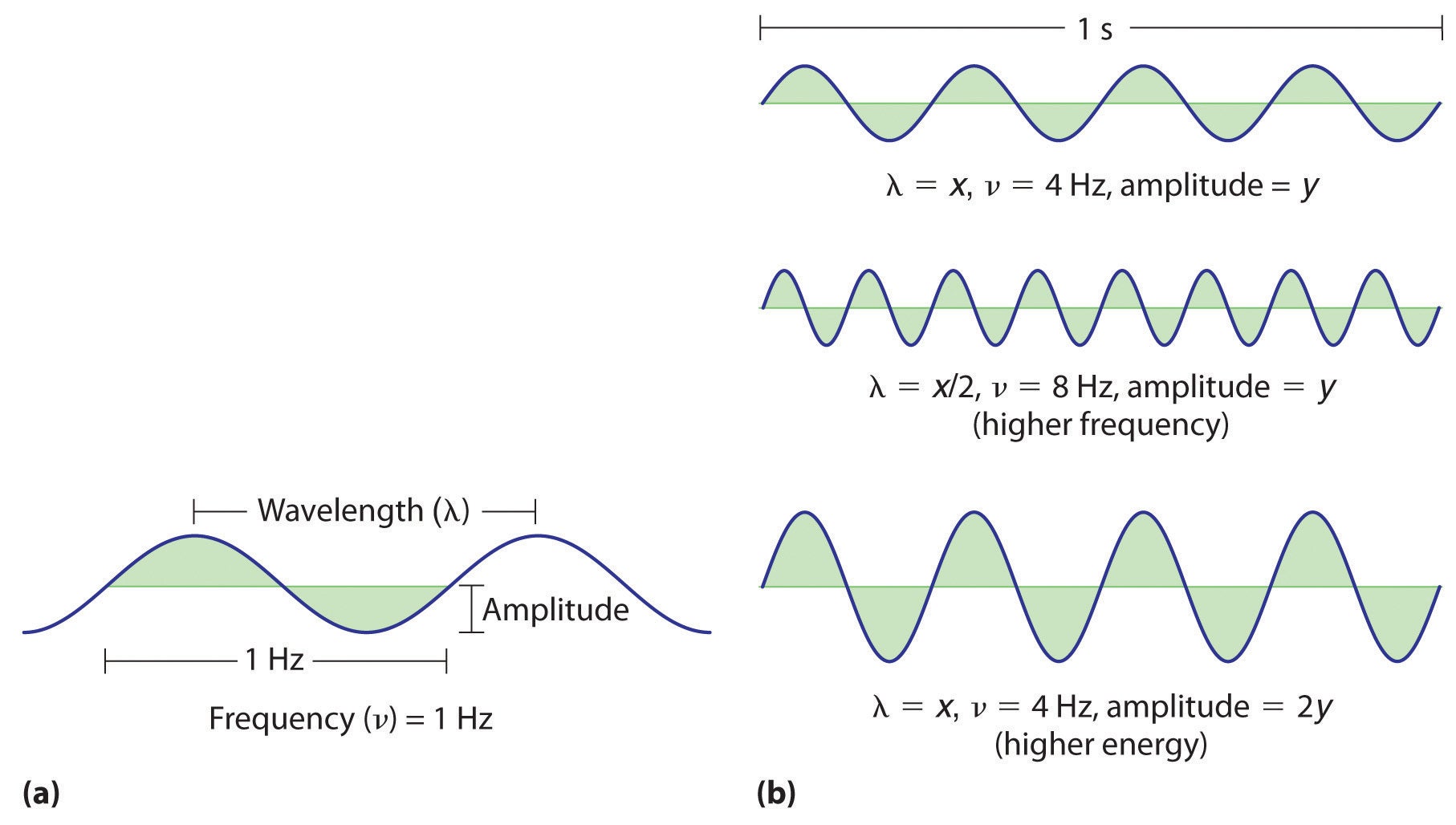
The first Wi-Fi standard used a frequency of 900 megahertz (MHz), meaning the wave twists 900 million times in a second, later adopting 2.4 GHz, and we now have Wi-Fi. Fi 5 GHz and 6 GHz. We use these cycles to encode information, and the higher the frequency, the more “packets” we can send in a second.
Wi-Fi bandwidth
Frequency is not the only limiting factor in information transfer, at least when it comes to Wi-Fi. We use multiple channels within these frequencies to transfer more data in parallel with each other. others. If we use a water pipe analogy, frequency is the speed at which we can move water through a fixed diameter pipe, while bandwidth is the diameter of the pipe.


We can achieve faster Wi-Fi by increasing the signal bandwidth and allowing more data to be transmitted simultaneously (more waves travel at the same time). So now that we know the basics, let's move on to Wi-Fi 6E.
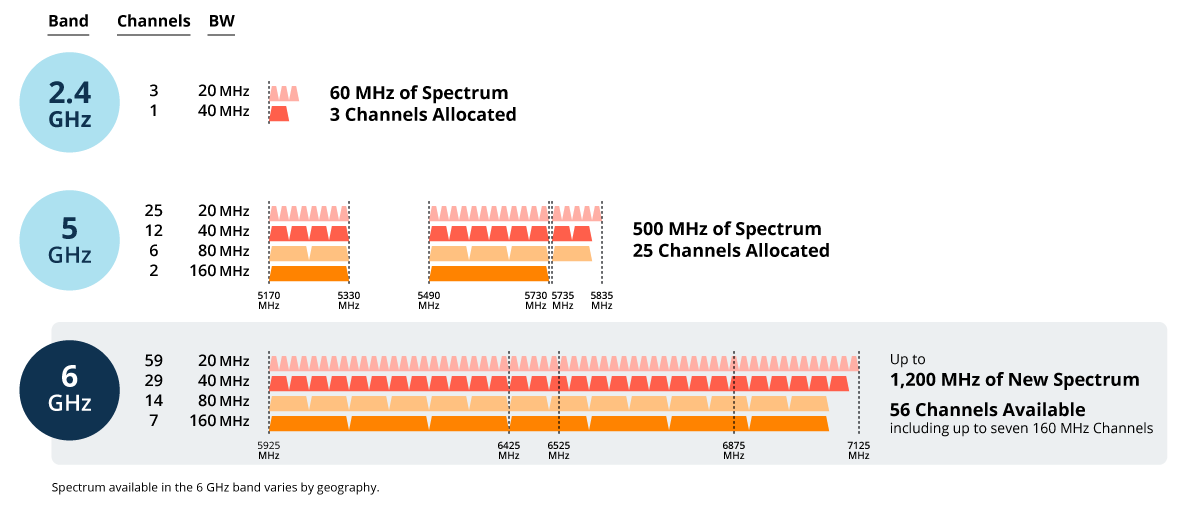
Wi-Fi 6E: The 6 GHz frequency band
Wi-Fi 6E is an improved version of the Wi-Fi 6 standard. It provides even more available channels to devices, resulting in less interference and faster speeds, and also adds the 6 GHz frequency to the table . Counterintuitively, Wi-Fi 6 uses the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies (the 6 in the name is just a coincidence in the numbering scheme).
By using the higher frequency, Wi-Fi 6E further increases data transfer speeds. But this is not the only advantage of the standard. It benefits from all the advantages of Wi-Fi 6.

Benefits of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E
9.6 Gbps on multiple channels. The bandwidth of Wi-Fi 6 is much wider (Wi-Fi 5 has 3.5 Gbps), or if we use our analogy above, the channel is larger. This allows more data to be transferred.
Transmission to multiple devices in the same window. This may seem obvious, but in previous Wi-Fi versions, different devices had to take turns waiting to receive packages over Wi-Fi. New OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) technology allows multiple devices to receive packages simultaneously via Wi-Fi in a single transmission window. This technology significantly improves the efficiency and speed of data transmission.
Lower latency. Wi-Fi 6 has up to 75% lower latency than Wi-Fi 5, which can be crucial for gamers and people who need the lowest possible latency without using wired communication. This is achieved in Wi-Fi 6 by implementing various techniques, such as the aforementioned OFDMA and Overlay Basic Service Sets (OBSS).
The latter means that the Wi-Fi router will not listen to a channel before transferring data in order to “see” if there is noise on that channel. Wi-Fi 6 allows routers to intelligently mark networks and channels with “colors“, and if a certain color is associated with a known network, the router does not need to wait and check for noise before to start the transmission.
Beam forming. It seems straight out of a science fiction movie, doesn't it? This is a rather simple and clever technology that allows Wi-Fi 6 routers to precisely pinpoint the location of other devices and send a focused beam of information in that direction instead of transmitting in all directions. directions. This technique not only enables faster data transfers but also increases system efficiency.
What do I need to get Wi-Fi 6E?


In order to benefit from all the benefits of Wi-Fi 6E, you basically need two things:
Wi-Fi 6E router: Get a Wi-Fi 6E router, which operates on the 6 GHz frequency band. This is a crucial part of getting the transfer speeds and benefits of Wi-Fi 6E.
Wi-Fi 6E compatible devices: Make sure your devices, such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other wireless gadgets, support Wi-Fi 6E. Newer devices are more likely to have this feature, so check the specifications or contact the manufacturer for more information.
Most modern flagship phones, such as the Galaxy S23 Plus and Ultra and iPhone 15 Pro models, support Wi-Fi 6E, but you should check the specifications before investing in a Wi-Fi 6E router and other devices.
Do I really need Wi-Fi 6E?
This is a difficult question. For most people, the speeds and bandwidth of Wi-Fi 5 would be enough, but if you want to be on the cutting edge, you need to get the latest and greatest technology. This is especially important if you have many wirelessly connected devices and need high transfer speeds and low latency.
















